COMPOSITION has developed a set of use cases for connecting data within a factory and between enterprises for a more efficient and flexible production. The result is applied business intelligence and automated market collaboration.
Data and services have become the key factor in manufacturing processes. The need to react on dynamically changing mark
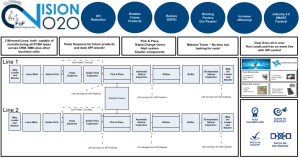
Boston Scientific’s future front end for PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) implementing COMPOSITION elements.
et demands is dramatically rising. Two of the most compelling tasks are to connect supply chain data and services between enterprises and to connect value chain data within a factory so that data can meaningfully support decision making.
To meet these needs, the COMPOSITION project has two main goals: To integrate data along the value chain inside a factory into one Integrated Information Management System (IIMS), and to create a (semi-)automatic ecosystem which extends the local IIMS concept to a holistic and collaborative system, incorporating and interlinking both the supply and the value chains.
Through a process of identifying the needs of the pilot sites, Boston Scientific Ltd in Ireland, ELDIA and Kleemann Hellas in Greece, COMPOSITION has developed scenarios and use cases for the system targeting two fields: Improvement of the internal production process (value chain/intra-factory approach) and efficient management of the supply chain (supply chain/inter-factory approach).
Use cases
In terms of the first focus area, business intelligence has been applied to improve the coordination mechanisms of the manufacturing processes. Use cases include:
- Detecting and registering process faults/anomalies early by visual tracking, identification and notification
- Performing predictive maintenance through an ongoing sensory overview of critical equipment
- Planning and tracking in real time the flow of material through the factory
- Automatically converting data to enable M2M communication
In the case of supply chains, manual management procedures and lack of automated, real-time data exchange often negatively influence overall performance. To this end, COMPOSITION will provide an automatic way of exchanging data and offering solutions through the ecosystem. Use cases here cover:
- Automating purchasing negotiations by facilitating the exchange of information between factories and solution providers
- Automating the logistics process for smooth communication with current suppliers
- Establishing a market place to develop, offer and purchase new solutions and services
Read more about the use cases in D2.1 Industrial Use Cases for an Integrated Information Management System
Tackling knowledge gaps in production
Central pilot sites will work on optimising their value chains inside the production plant. On top of this, some will also look to strengthen the interaction with the supply chain:
- Boston Scientific Ltd in Ireland is the largest plant in the Boston Scientific Corporation. It is the sole manufacturer of pulse generators (pacemakers, implantable cardiac defibrillators) in the group. Boston Scientific aims to leverage COMPOSITION tools and technologies to tackle real knowledge gaps within their business. These can improve its current method of manufacturing and enable it to remain the prime manufacturer of pacemakers and defibrillators.
-

The Kleemann factory complex in Kilkis, Greece
Kleemann in Greece manufactures and trades complete lift systems. The range of products includes domestic and commercial lift systems, including car parking and multi-storey building lift systems. Three departments of the Kleemann plant will be involved in the COMPOSITION pilot: the car slide (intra-factory application), the piston-cylinder and the power unit department (inter-factory application). The aim is to save cost on material as well as strengthen the intercommunication between the different enterprises involved in collecting and selling the scrap metal from Kleemann’s production.
- ELDIA is the largest waste management company in Northern Greece and their activities cover the entire range of solid waste management, both in the public and industrial sectors. The IoT-isation of the physical site of ELDIA is investigated. The scope is to implement the applied business intelligence of the COMPOSITION IIMS to enable and optimise communication and collaboration within the company itself.
Automated market collaboration in the supply chain
In terms of interaction with companies in the supply chain, Kleemann will engage with different actors using the COMPOSITION ecosystem and its marketplace for collaboration. Three of them will function as satellite pilots:
- ATLANTIS Engineering (Greece) is an ICT SME with experience in the industrial manufacturing domain; mainly in decision support for management and optimisation of production activities and assets life cycle; in design, interconnection and implementation of models and protocols for manufacturing, and in streamlining of various maintenance related processes. They will be providing software and services via the COMPOSITION ecosystem.
- Nextworks (Italy) is a company working in the areas of IoT, Embedded Systems, Big Data, Networks, Digital video, Control and Automation systems. Nextworks will be providing services for monitoring and managing the production line. Decision processes inside the production line will also be enhanced, using professional analysis tools offered by the COMPOSITION marketplace.
- ELDIA undertakes the collection, transportation, sorting and processing of all commercial and industrial waste in order to recover materials (paper, wood, plastics, metal, pallets and glass) and offer them to the recycling industries. It provides services and solutions to the management of solid waste and disposal issues. ELDIA handles the waste and recycling of material from Kleemann’s facilities.
Moving from need to solution
Developing an integrated information management system is a very complex undertaking. Hence, COMPOSITION has applied an iterative process, going through a phase of defining scenarios and gathering user requirements which are continuously refined.
So far, the project has conducted scenario workshops with all pilot sites in order to first understand the current situation and secondly, to identify how and where the COMPOSITION ecosystem can be used to optimise manufacturing and logistics processes. This activity has resulted in a number of industrial scenarios for the pilots and related use cases which are described in D2.1 Industrial Use Cases for an Integrated Information Management System.
Based on the scenarios and use cases, initial user requirements have been elicited and documented in D2.2 Initial Requirements Report. Due to the iterative approach of the development work in the project, the scenarios and use cases will be revisited and revised during the project lifetime.